01、马黛茶简介
马黛茶由南美洲独有的马黛树叶精制而成,在阿根廷等南美国家拥有400多年的饮用历史,被阿根廷誉为“国宝”、“国茶”,与咖啡、茶(红茶、绿茶等)并称为“世界三大茶”。马黛茶叶又名巴拉圭冬青叶,马黛茶经过采摘、烘烤、干燥等工艺制成。
马黛茶似茶非茶,不同于中国的饮茶习惯,阿根廷喝马黛茶的传统方法需要吸管和茶壶。一般是将马黛茶泡在竹筒或挖空的葫芦等圆筒状杯子里,并配以带有过滤作用的金属吸管。吸管的一头有小孔进行过滤,另一头用于饮茶,轻轻吸允过滤后饮用。
1.1马黛茶的功效成分
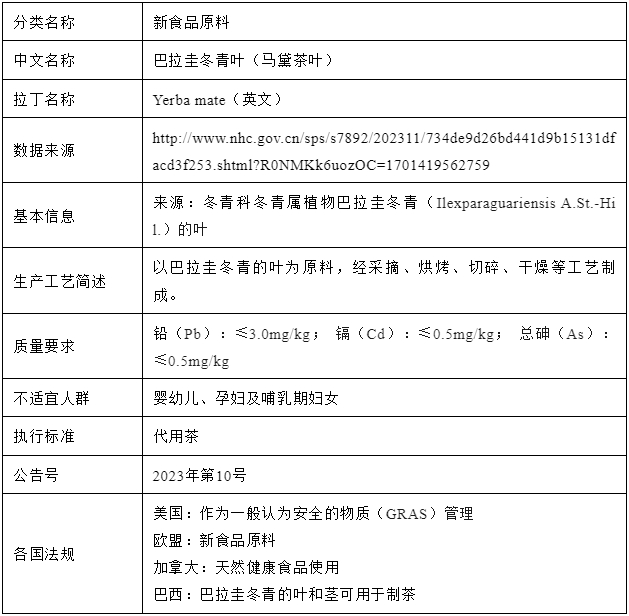
2023年12月01食品安全标准与监测评估司发部的新食品原料解度中指出,马黛茶主要营养成分为碳水化合物、粗纤维、蛋白质、脂肪、维生素、矿物质和氨基酸等,且含有少量的多酚、黄酮和皂苷类等物质。现代研究也表明,马黛茶中含有丰富的化学成分,以下表格将讲述马黛茶的功效成分[1-3]:

1.2马黛茶功效作用
通过收集相关研究,表2汇总马黛茶的功效作用及机理[4-5]。

表2马黛茶功效作用及机理
1.3马黛茶临床研究现状
在中国知网以“马黛茶”为关键词检索,共有64篇文献,主要研究为马黛茶的功效成分、功效作用及提取工艺等。在国外马黛茶的研究较深入,故以Yerba Mate(马黛茶),Anti-inflammatory(抗炎),metabolic(代谢),antioxidant(抗氧化),physiological effects(生理作用),disease preventive effects(疾病预防效果),cardiovascular or cardioprotective effects(心血管或心脏保护作用)为关键字,检索PubMed,Web of Science等数据库,汇总了部分马黛茶的临床研究,见表3。
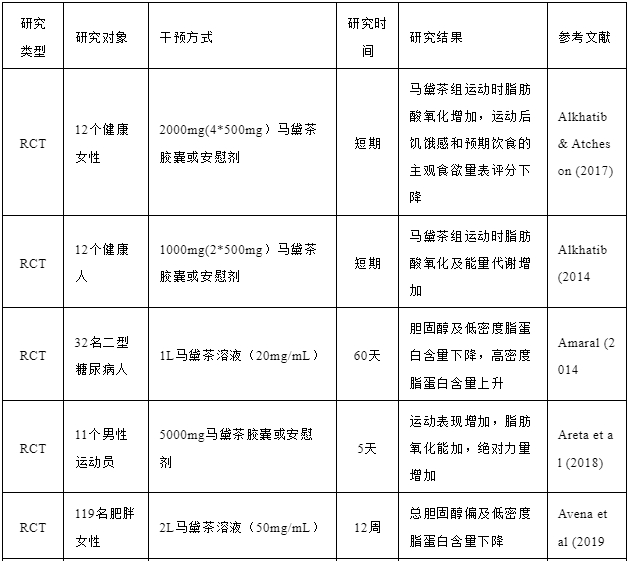
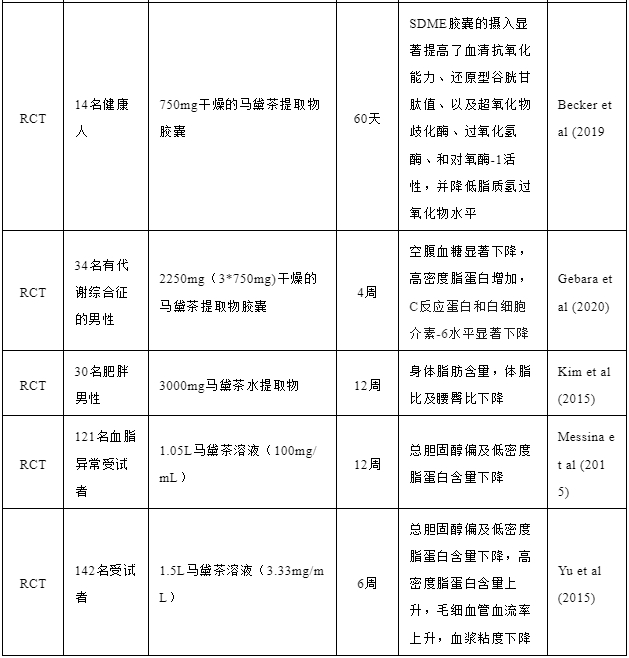
表3马黛茶临床研究汇总[6-15]
02、马黛茶市场应用
马黛茶主要在阿根廷国家有食用历史,在国外市场应用广泛。以下内容为收集到的国外马黛茶制品,食品类型主要为茶制品及粉剂。
目前在国内比较知名的马黛茶生产商为PLAYADITO马黛茶,由阿根廷克罗尼亚列比格农业合作社创立于1926年,于2023年进入中国市场。
03、总结
巴拉圭冬青叶(马黛茶叶)作为阿根廷国宝,食用历史悠久,根据国内外研究表明,马黛茶在血脂管理、抗氧化、体重管理、心血管疾病保护等方面均有作用。马黛茶作为新食品原料引入中国,意味着植物类功效作用的原料又增加一员,亦可为功能食品的发展做出贡献。
参考资料:
[1]吴俊玲,高红莉,刘昭纯.马黛茶及有效成分研究概况[J].山东中医杂志, 2010(9):3.DOI:CNKI:SUN:SDZY.0.2010-09-041.
[2] Dall’Orto VC. Comparison of tyrosinase biosensor and colorimetric method for polyphenol analysis in different kinds of teas [J]. Anal Lett,2005,38:19-33.
[3] Carini M,Facino RM,Aldini G,et al. Characterization of phenolic antioxidants from Mate(Ilex paraguayensis)by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Commun in Mass Spec,1998,12:1813-1819.
[4]韩晴,杨英兰,韩茜茜,等.马黛茶成分及疗效的研究进展[J].山西医药杂志, 2020, 49(4):4.DOI:CNKI:SUN:SXYY.0.2020-04-020.
[5]于少泓,吴俊玲,刘昭纯.马黛茶临床作用研究进展[J].山东中医药大学学报, 2010(4):3.DOI:CNKI:SUN:SDYX.0.2010-04-040.
[6]Alkhatib A, Atcheson R. Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) metabolic, satiety, and mood state effects at rest and during prolonged exercise. Nutrients. 2017;9:882
[7]Alkhatib A. Yerba Mate (Illex Paraguariensis) ingestion augments fat oxidation and energy expenditure during exercise at various submaximal intensities. Nutr metab (Lond). 2014;11:42.
[8] Amaral CL. Effect of cha mate (Ilex paraguariensis) on glycemic and lipid profile, inflammatory markers, and endothelial function of individuals with type 2 diabetes . Florianopolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil: Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC); 2014
[9] Areta JL, Austarheim I, Wangensteen H, et al. metabolic and performance effects of yerba mate on well-trained cyclists. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50:817–826.
[10]】Avena V, Messina D, Corte C, et al. Association between consumption of yerba mate and lipid profile in overweight women. Nutr Hosp. 2019;36:1300–1306.
[11] Becker AM, Cunha HP, Lindenberg AC, et al. Spray-dried yerba mate extract capsules: clinical evaluation and antioxidant potential in healthy individuals. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2019;74:495–500
[12] Gebara KS, Junior AG, Palozi RAC, et al. A randomized crossover intervention study
on the effect a standardized mate extract (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) in men predisposed to cardiovascular risk. Nutrients. 2020;13:14
[13] Boaventura BCB, Di Pietro PF, Stefanuto A, et al. Association of mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) intake and dietary intervention and effects on oxidative stress biomarkers of dyslipidemic subjects. Nutrition. 2012;28:657–664
[14] Messina D, Soto C, Mendez A, et al. Lipid-lowering effect of mate consumption in dyslipidemic individuals [in Spanish]. Nutr Hosp. 2015;31:2131–2139. [10.3305/ nh.2015.31.5.8386]
[15] Yu S, Yue SW, Liu Z, et al. Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) improves microcirculation of volunteers with high blood viscosity: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2015;62:14–22
来源:食品伙伴网食品研发创新服务中心,作者:Kate,食品专业硕士,高级公共营养师,现从事食品研发工作。图片来源:创客贴会员。
提醒:文章仅供参考,如有不当,欢迎留言指正和交流。且读者不应该在缺乏具体的专业建议的情况下,擅自根据文章内容采取行动,因此导致的损失,本运营方不负责。如文章涉及侵权或不愿我平台发布,请联系处理。










